Weighing the pros and cons of early delivery in women with preeclampsia
Planned delivery or expectant management in preeclampsia: an individual participant data meta-analysis
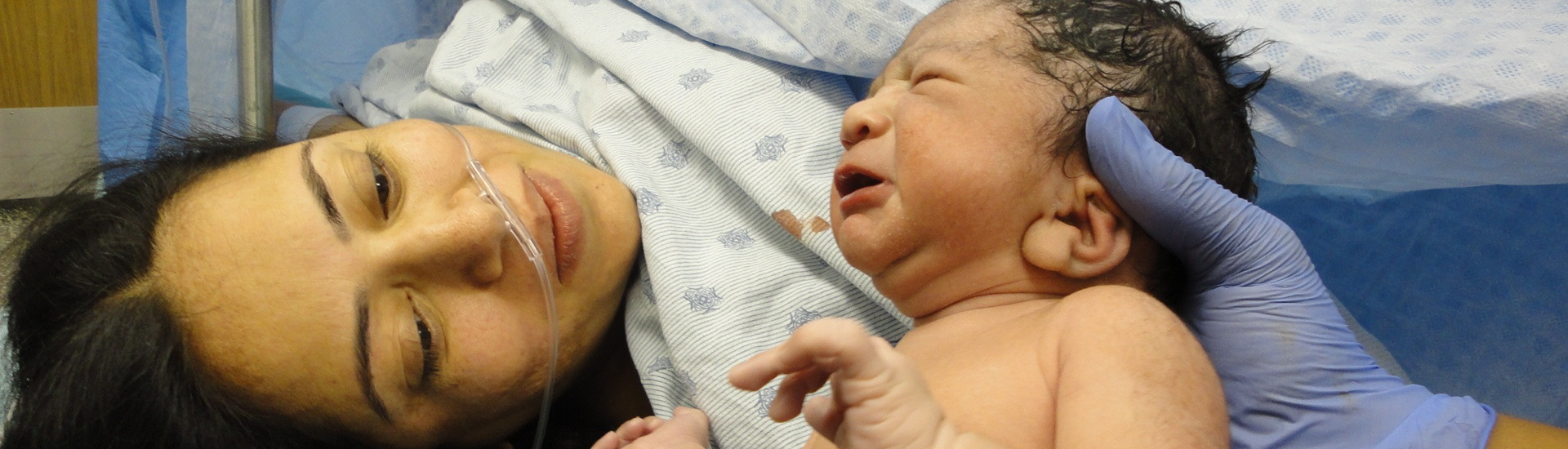
Delivery of the baby and the placenta is still the only definitive management for preeclampsia, and planned delivery is recommended for all women with preeclampsia who are 37 weeks pregnant or more. However, for women who are 34-36 weeks pregnant with preeclampsia, immediate delivery is not recommended due to the risks it may present to the baby. Healthcare providers will typically follow “expectant management” for these women, monitoring them closely until delivery is necessary because of possible risks for the baby from early preterm birth. Several smaller studies have explored this recommendation for expectant management, asking whether planned delivery among women with preeclampsia between 34-36 weeks of pregnancy is more beneficial for mother and baby compared to expectant management. In this study, researchers combined the data from several of these studies (1,790 participants across six different research studies) in a meta-analysis to ask if planned delivery between 34-36 weeks of pregnancy in women with preeclampsia can reduce complications for the mother and her baby. Researchers created a composite outcome to answer their question, a combination of several possible clinical complications related to preeclampsia and early delivery.
The results showed that planned delivery (compared to “expectant management”) at 34 weeks or later reduced risk for complications in the mother as well as the decreased the likelihood the baby would be small for their gestational age. However, planned early delivery was found to increase the risk for short-term respiratory complications in the baby.
Take home message: This meta-analysis showed that planned delivery in women 34-36 weeks pregnant with preeclampsia has both benefits and risks. These risks and benefits should be consider by clinicians caring for women with preeclampsia and discussed with patients when presenting management options for her pregnancy.
Link: https://www.ajog.org/article/S0002-9378(22)00315-5/fulltext
Citation: Beardmore-Gray A, Seed PT, Fleminger J, Zwertbroek E, Bernardes T, Mol BW, Battersby C, Koopmans C, Broekhuijsen K, Boers K, Owens MY, Thornton J, Green M, Shennan AH, Groen H, Chappell LC. Planned delivery or expectant management in preeclampsia: an individual participant data meta-analysis. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2022 Apr 26:S0002-9378(22)00315-5. doi: 10.1016/j.ajog.2022.04.034. Epub ahead of print. PMID: 35487323.
About Research Roundup
Each quarter, our team of researchers reviews the most current studies related to hypertensive disorders of pregnancy and selects those studies they feel will be of greatest interest to our community to summarize.
Special thanks to our volunteer research team, who under the leadership of Dr. Elizabeth Sutton, make Research Roundup possible: Alisse Hauspurg, MD Felicia LeMoine, and MD Jenny Sones, PhD, DVM.
Related Articles
Recent findings in preeclampsia research have shown that preeclampsia likely has at least two variants – an early onset and a late onset variant. Early onset is typically defined as before 34 we...
Preeclampsia is a pregnancy complication marked by new-onset high blood pressure and signs of stress on organs such as the kidneys, liver, and brain. While much attention is often given to preterm dis...

Preeclampsia is a serious problem that can happen during pregnancy. It often affects the brain and can cause headaches, vision problems, strong reflexes, and seizures (called eclampsia). In this study...

Pregnancy offers a unique window into a woman’s future heart and cardiovascular health. Conditions such as hypertensive disorders of pregnancy (HDP) which include gestational hypertension, preec...

Heart disease, also called cardiovascular disease (CVD), is becoming more common in young women across the United States. Hypertensive disorders of pregnancy (HDP) is a group of conditions that includ...

